Overview
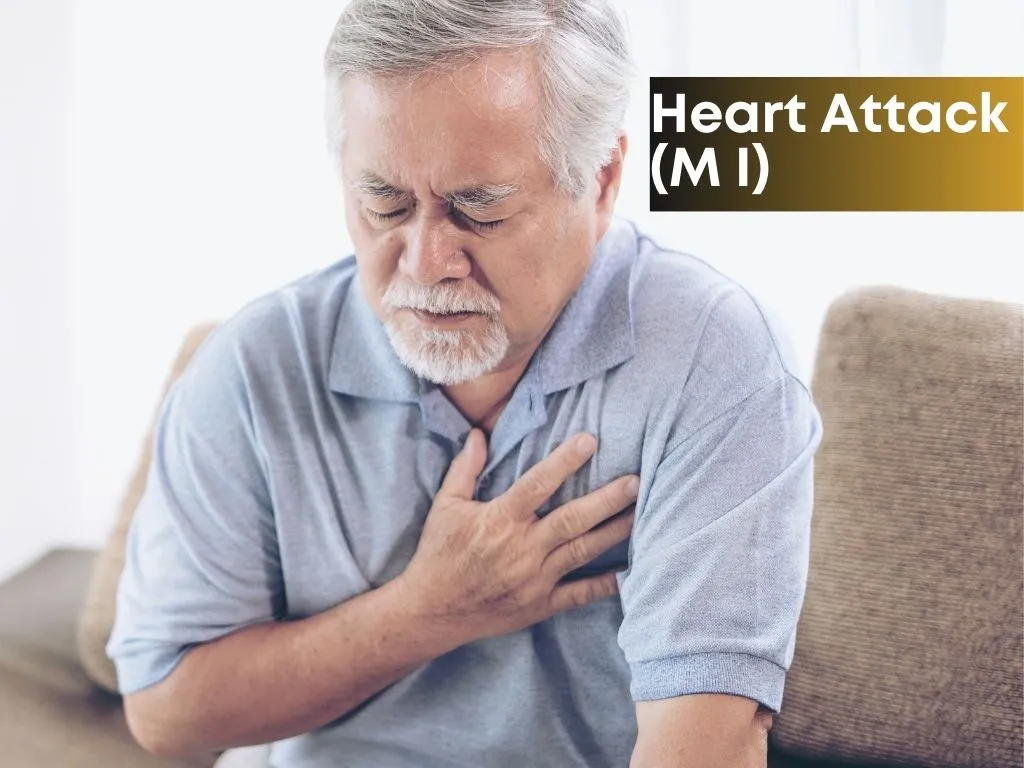
A Myocardial Infarction, also known as a heart attack, is a serious medical condition that occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked. This blockage can be caused by a build-up of plaque in the coronary arteries, which are the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart.
Causes
Myocardial Infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, has several potential causes, but the most common one is Coronary Artery Disease (CAD). Here's a breakdown of the causes:
Coronary artery disease (CAD)High blood pressureHigh cholesterolSmoking.DiabetesObesityInactivityStressDrug abuse
Less common causes of myocardial infarction:
Spasm of a coronary arterySevere injury or traumaCertain infectionsCongenital heart defects:
Symptoms
Chest pain or discomfortNausea, vomiting, or indigestion.Feeling lightheaded or dizzy.Cold sweat.Fatigue.
Treatment: Modern Medicine
Emergency Treatment:
Immediate medical attention is crucial.In emergency administer Aspirin to help prevent further blood clotting.Oxygen therapy may be provided to improve oxygen levels in the blood.
Medications:
Thrombolytics (Clot-busting drugs) Antiplatelet medicationsAnticoagulants (blood thinners)Beta-blockersACE inhibitorsStatins Pain relievers
Interventional Procedures:
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
Healthy Diet:
Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fatsLimit intake of saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and processed foods.Increase fiber intake to help lower cholesterol levels and improve digestion.
Herbal Supplements:
Some herbal supplements, such as garlic, hawthorn, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Caution
Monitor Blood Pressure and Cholesterol LevelsQuit SmokingLimit Alcohol IntakePotential Risks and Side Effect.
Prevention
Know the symptomsHave an emergency planKeep medications handyConsider CPR training
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team


















.jpg.webp)
