Overview
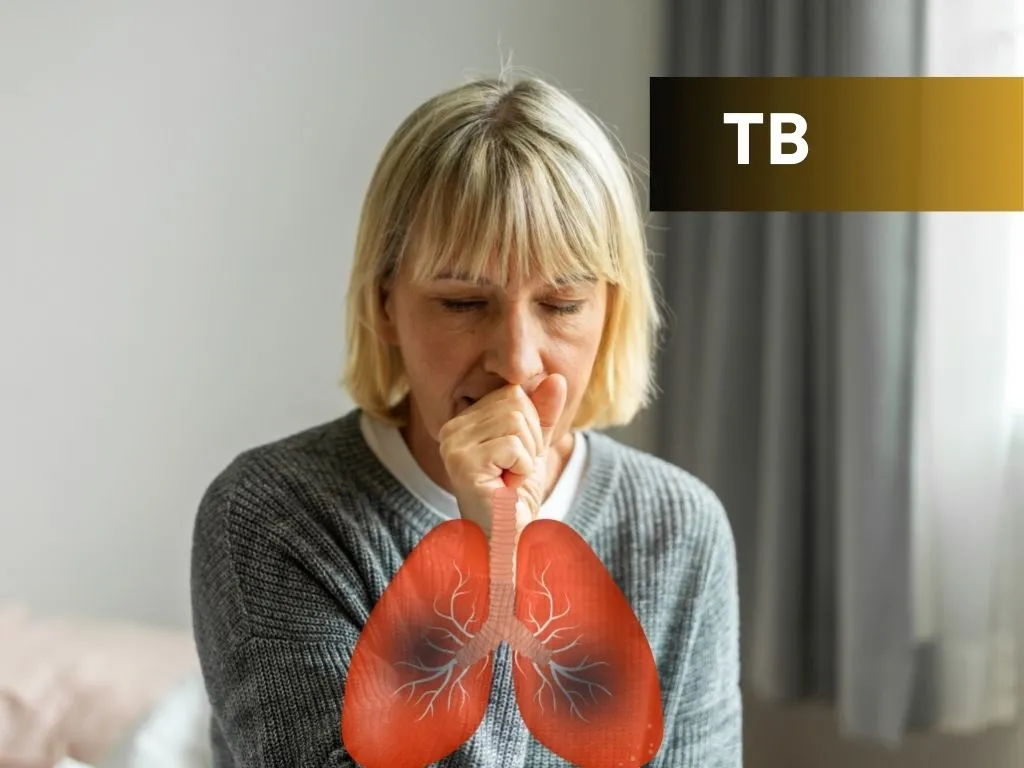
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially serious infectious disease caused by
the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs
but can also affect other parts of the body, such as the kidneys,
spine, and brain. TB spreads through the air when an infected person
coughs or sneezes, releasing tiny infectious droplets that can be
inhaled by others.
Causes
Some common causes and risk factors for TB include:
Close Contact with an Infected PersonWeak Immune SystemOvercrowded and Poorly Ventilated EnvironmentsSubstance AbuseMalnutritionAgeTravel or Migration to High TB Burden AreasHealthcare SettingsDrug ResistanceGenetic Factors
Symptoms
The symptoms of tuberculosis (TB) can vary depending on whether the infection is latent (inactive) or active.
Latent TB Infection (LTBI):
Latent TB infection typically doesn't cause any symptoms.
Active TB Disease:
Persistent CoughChest PainFatigue and WeaknessFeverNight SweatsLoss of AppetiteShortness of BreathChillsSwollen Lymph Nodes
Treatment: Modern Medicine
Combination FormulationsDirectly Observed Therapy (DOTDrug Resistance Testing
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
Healthy DietHerbal TeasHoneyGarlicTurmericMilk with TurmericRest and Stress ReductionSteam InhalationSaltwater Gargle
Caution
Consult with a Healthcare ProfessionalDo Not Replace Medical TreatmentPotential Interactions with TB MedicationsAdverse Effects
Prevention
VaccinationIdentifying and Treating Latent TB InfectionEarly Detection and Treatment of Active TBInfection Control MeasuresContact Tracing and Screening
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team


















.jpg.webp)
