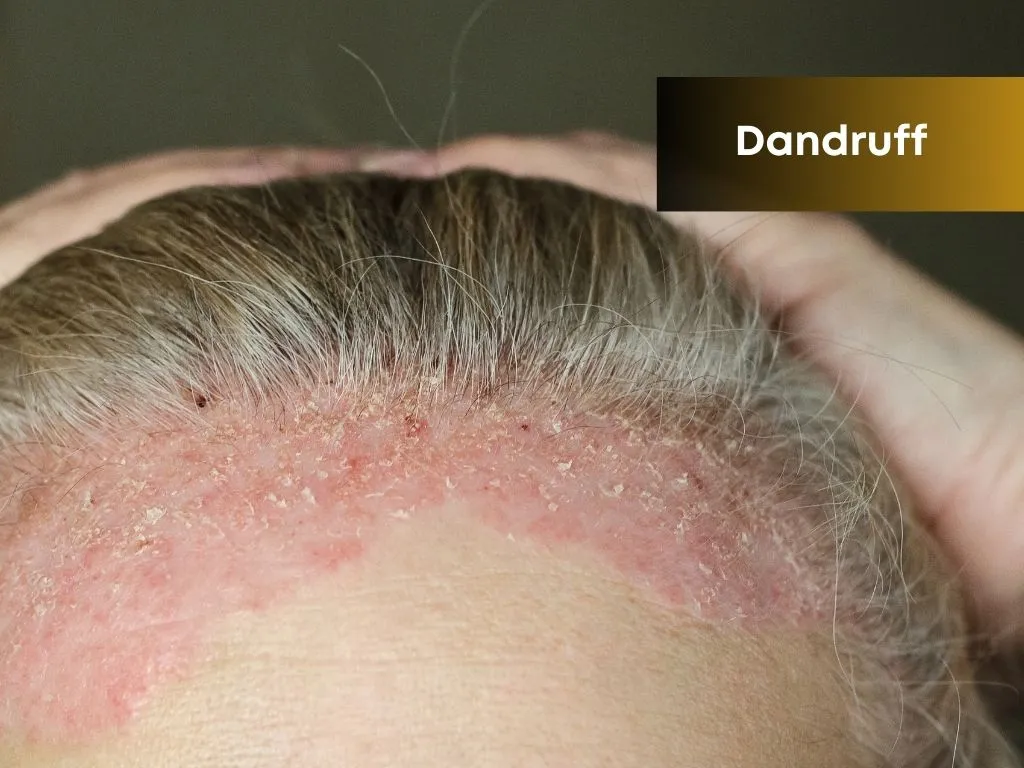
Dandruff (Severe / Seborrheic Dermatitis)
-
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team
- 22 September 2025
Overview
Seborrheic dermatitis may flare in cold weather, stress, or oily skin conditions. It is not contagious, but it is chronic and recurrent.
Causes
- Malassezia yeast overgrowth
- Excess sebum production
- Immune dysfunction
- Cold, dry climate
- Neurological diseases (e.g., Parkinson’s)
Symptoms
- Greasy white or yellowish flakes
- Itchy, red, inflamed scalp
- Crusting or thick patches in severe cases
- Scalp sensitivity or burning
Treatment: Modern Medicine
- Diagnosis: Clinical exam (may mimic psoriasis or eczema)
- Treatment:
- Medicated shampoos (ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, zinc pyrithione)
- Topical antifungals and mild corticosteroids
- Salicylic acid for thick scales
- Regular hair washing and scalp hygiene
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
- Ayurveda: Nimbadi taila, Khadirarishta, Triphala churnam for detox
- Siddha: Herbal oils (Neem, Pavala parpam), hair packs
- Unani: Zimad application, Arq-e-Gulab hair rinse
- TCM: Herbal scalp cleansers, acupuncture for sebum balance
- Homeopathy: Thuja, Graphites, Sulphur
- Nutraceuticals: Biotin, Zinc, Omega-3, Vitamin D
Caution
- Avoid frequent steroid use—can thin skin
- Scratching worsens infection risk
Prevention
- Maintain scalp hygiene
- Avoid harsh shampoos and hair products
- Manage stress and diet


















.jpg.webp)
