Diabetic Retinopathy
-
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team
- 22 September 2025
Overview
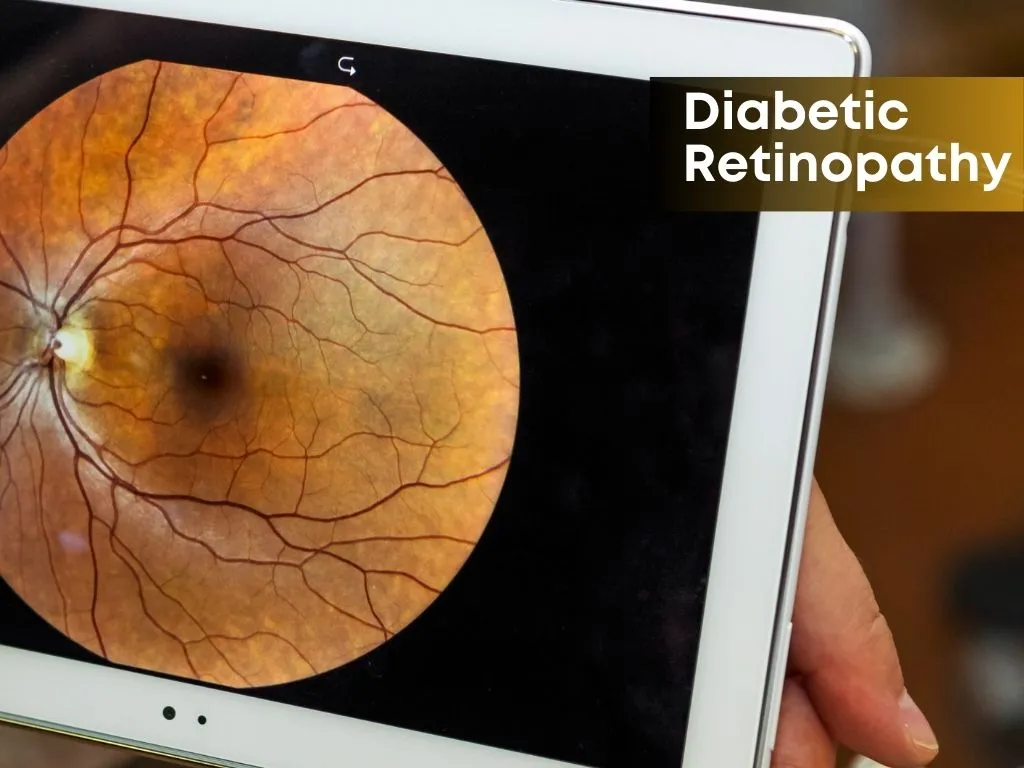
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes complication that affects the eyes. It's caused by damage to the blood vessels of the retina, which is the tissue located at the back of the eye that senses light and helps to transmit images to the brain.
In people with diabetes, high levels of blood sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina over time. There are two main types of Diabetic retinopathy:
Causes
Symptoms
Treatment: Modern Medicine
Several modern medical interventions and treatments are available to manage diabetic retinopathy:
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
Caution
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious condition that can lead to vision loss. This serves as a caution to individuals with diabetes to be aware of the risks and the importance of preventive measures.



















.jpg.webp)
