Gout
-
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team
- 23 September 2025
Overview
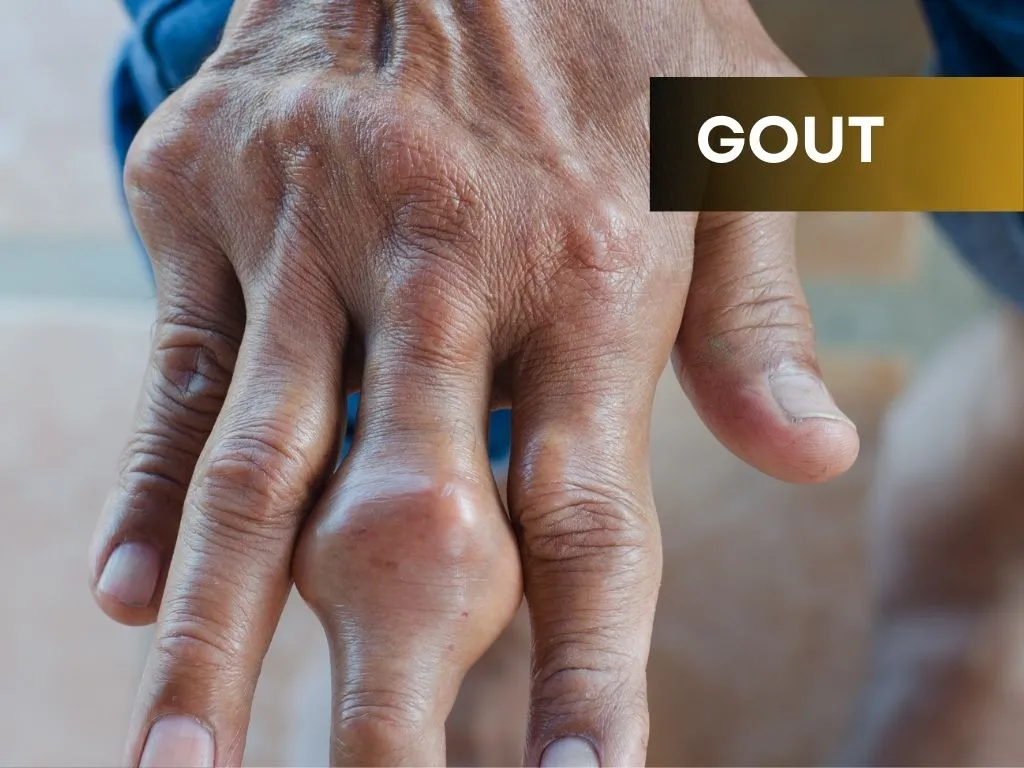
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, leading to intense pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness. Uric acid is a waste product that is normally dissolved in the blood and eliminated from the body through urine. However, in people with gout, either the body produces too much uric acid or it doesn't eliminate enough of it, causing it to build up and form crystals in the joints.
Causes
The most commonly affected joint is the big toe, but gout can also affect other joints such as the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers. Gout attacks often come on suddenly and can be extremely painful, with the affected joint feeling hot, swollen, and tender to the touch.
The primary cause of gout is an elevated level of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia.
Several factors can contribute to the development of hyperuricemia and gout, including:
Symptoms
The symptoms of gout typically manifest as sudden and intense pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness in the affected joint(s). The most commonly affected joint is the big toe, but gout can also occur in other joints such as the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers.
Treatment: Modern Medicine
Medications for Acute Attacks:
Medications to Lower Uric Acid Levels:
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
Caution


















.jpg.webp)
