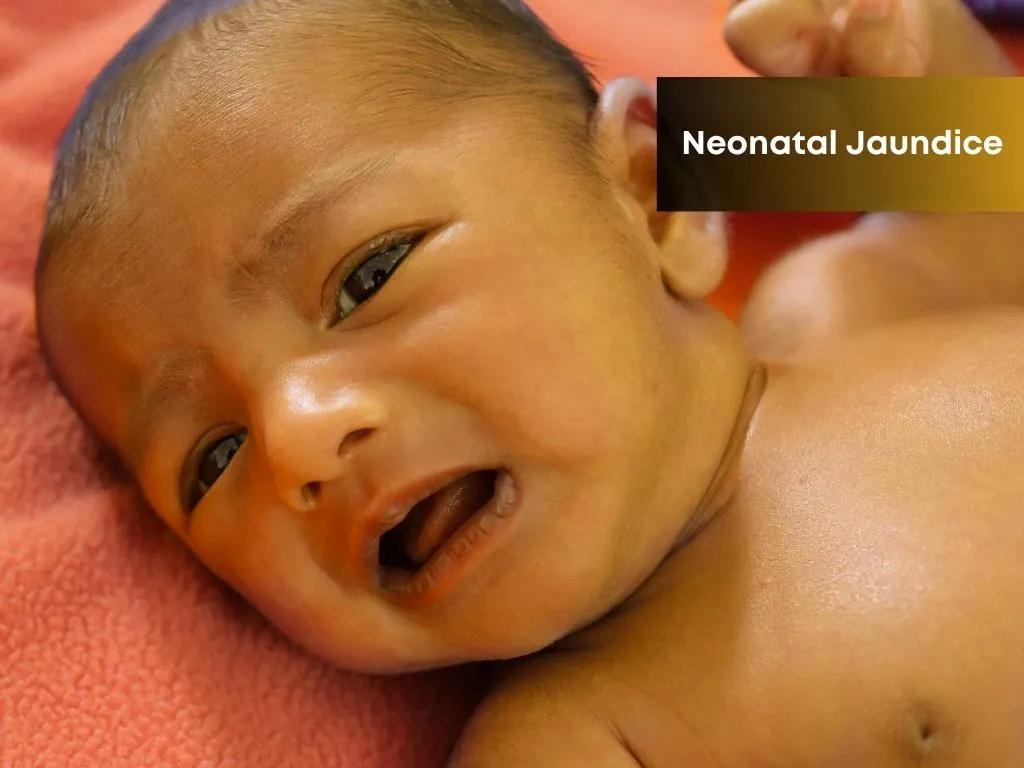
Neonatal Jaundice
-
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team
- 22 September 2025
Overview
Seen in 50–60% of newborns. Most cases are physiological but some may be pathological due to blood group incompatibility or liver issues.
Causes
- Immature liver enzyme function
- ABO or Rh incompatibility
- Bruising or birth trauma
- Breastfeeding jaundice (due to poor intake)
Symptoms
- Yellowing of skin and eyes
- Sleepiness or poor feeding
- High-pitched cry (in severe cases)
- Starts at face, spreads down body
Treatment: Modern Medicine
- Diagnosis: Serum bilirubin levels, blood group, Coombs test
- Treatment:
- Phototherapy (blue light)
- Exchange transfusion (severe cases)
- Encourage frequent breastfeeding
- Monitor bilirubin hourly in high-risk cases
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
- Ayurveda: Haritaki, Guduchi, and mild detox herbs (post phototherapy support)
- Siddha: Liver tonic drops (Siriya Siruthai)
- Unani: Sharbat-e-Banafsha, cooling herbs
- TCM: Yin chen hao tang, gentle liver support
- Homeopathy: Chelidonium, Nux vomica (only with pediatric approval)
- Nutraceuticals: Vitamin D drops, support for breastfeeding mother
Caution
- Severe jaundice can cause brain damage (kernicterus)
- Monitor all babies, especially preterm or those with risk factors
Prevention
- Early breastfeeding initiation (within 1 hour of birth)
- Monitor newborn for yellowing daily for first week
- Rh screening in pregnancy



















.jpg.webp)
