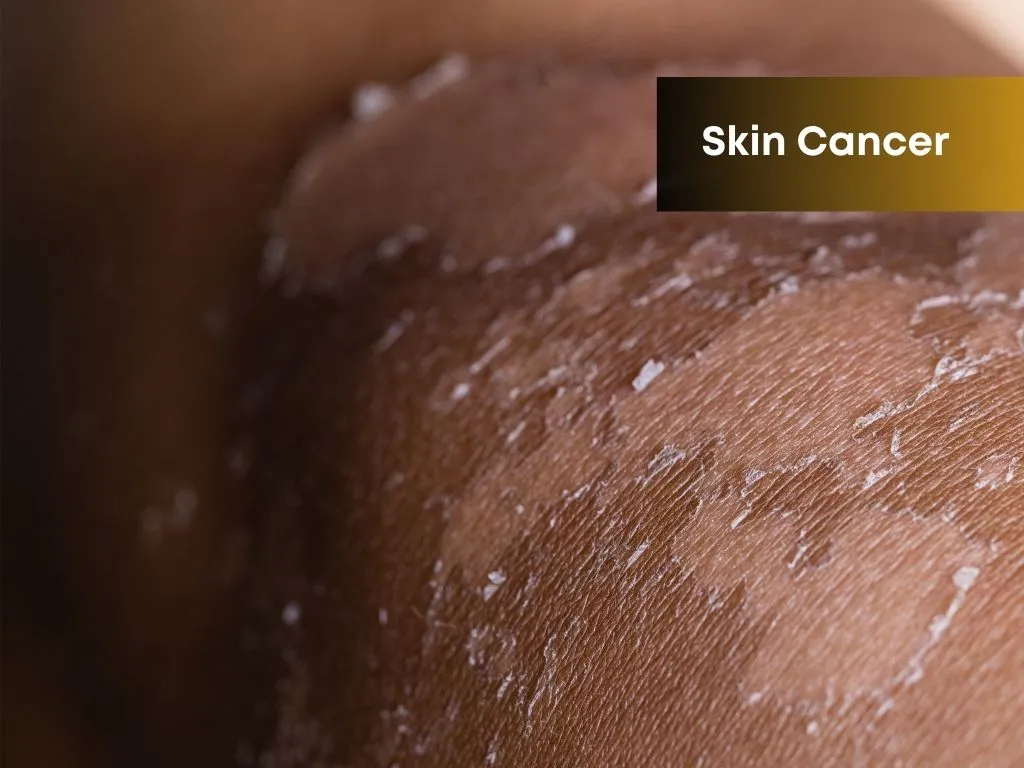
Skin Cancer
-
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team
- 22 September 2025
Overview
Early detection saves lives. Melanoma, though less common, is responsible for most deaths. Risk increases with fair skin, sun exposure, and family history.
Causes
- Prolonged sun or tanning bed exposure
- Genetic predisposition
- Previous radiation therapy
- Immunosuppression
Symptoms
- New or changing mole (ABCDE signs)
- Non-healing ulcer
- Red, scaly patch
- Dome-shaped growth with blood vessels
- Itchy, bleeding skin lesions
Treatment: Modern Medicine
- Diagnosis: Dermoscopy, skin biopsy
- Treatment:
- Surgical excision (first-line)
- Mohs surgery for facial lesions
- Radiotherapy or topical chemotherapy (5-FU)
- Immunotherapy for advanced melanoma
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
- Ayurveda: Neem, Turmeric, Kanchanar Guggulu for abnormal growth
- Siddha: Parpam formulations and detoxifying herbs
- Unani: Tumor inhibitors (Qurs Kushta, Majoon)
- TCM: Oldenlandia diffusa, Scutellaria baicalensis
- Homeopathy: Thuja, Carcinosin, Arsenicum album (supportive)
- Nutraceuticals: Vitamin D, Selenium, Green tea extract, Lycopene
Caution
- Melanoma spreads fast — act early
- Don’t ignore new or changing skin spots
Prevention
- Use sunscreen (SPF 30+)
- Avoid sun exposure 10 AM–4 PM
- Wear protective clothing and hats
- Annual skin check for high-risk people

















.jpg.webp)
