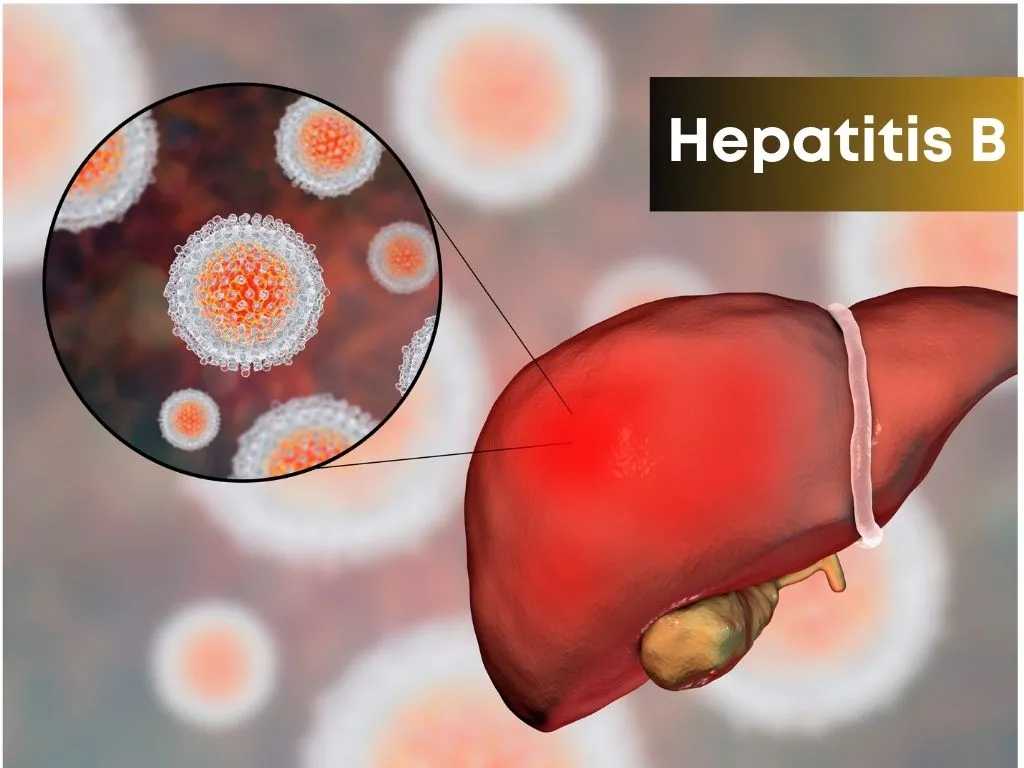
Hepatitis B
-
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team
- 22 September 2025
Overview
Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood and body fluids. While some recover spontaneously, others develop lifelong infection requiring regular monitoring
Causes
- Blood transfusions or contaminated needles
- Unprotected sexual contact
- Mother-to-child during childbirth
- Tattooing or piercing with unsterile instruments
Symptoms
- Fatigue, jaundice
- Abdominal pain, dark urine
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea, joint pain
- In chronic cases: liver enlargement, cirrhosis signs
Treatment: Modern Medicine
- Diagnosis: HBsAg, HBeAg, Anti-HBs, HBV DNA PCR
- Treatment:
- Acute: Supportive care
- Chronic: Antiviral therapy (Tenofovir, Entecavir)
- Liver function monitoring every 6–12 months
- Liver transplant in end-stage cases
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
- Ayurveda: Bhumyamalaki, Katuki, Kalmegh – liver detox and antiviral properties
- Siddha: Keelanelli, Sirukanpeelai for liver strength
- Unani: Sharbat-e-Unnab, Majoon Dabeedul Ward
- TCM: Schisandra, Milk Thistle, Rehmannia
- Homeopathy: Chelidonium, Carduus marianus
- Nutraceuticals: Milk thistle extract, NAC, Vitamin E, Selenium
Caution
- HBV is highly contagious via blood contact
- Alcohol accelerates liver damage in HBV patients
- Screening of family members recommended
Prevention
- Hepatitis B vaccine (birth + 3 doses)
- Avoid sharing razors, needles
- Safe sex and screened blood transfusions


















.jpg.webp)
